
Android applications with hundreds of thousands and thousands of downloads are susceptible to attacks that allow malicious apps to steal contacts, login credentials, private messages, and other delicate information. Safety organization Check Issue claimed that the Edge Browser, the XRecorder video clip and screen recorder, and the PowerDirector video editor are among people influenced.
The vulnerability truly resides in the Google Engage in Core Library, which is a collection of code created by Google. The library allows apps to streamline the update method by, for instance, receiving new versions for the duration of runtime and tailoring updates to an individual app’s certain configuration or a distinct telephone design the application is managing on.
A main vulnerability
In August, security business Oversecured disclosed a protection bug in the Google Play Core Library that allowed a person put in app to execute code in the context of any other app that relied on the susceptible library version.
The vulnerability stemmed from a listing traversal flaw that authorized untrusted resources to copy documents to a folder that was intended to be reserved only for reliable code obtained from Google Participate in. The vulnerability undermined a main protection created into the Android operating technique that helps prevent a single app from accessing information or code belonging to any other app.
Here’s an impression that illustrates how an attack may well do the job:
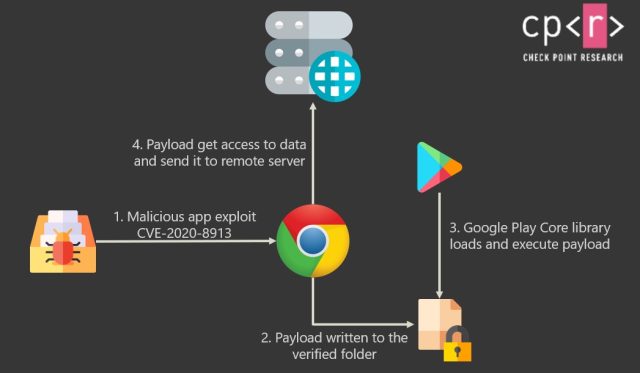
Check out Point
Google patched the library bug in April, but for susceptible apps to be fastened, builders need to initial down load the updated library and then include it into their application code. According to study findings from Examine Position, a nontrivial selection of builders continued to use the vulnerable library edition.
Test Place scientists Aviran Hazum and Jonathan Shimonovich wrote:
When we combine well known programs that employ the Google Perform Core library, and the Nearby-Code-Execution vulnerability, we can evidently see the threats. If a destructive application exploits this vulnerability, it can acquire code execution within preferred applications and have the exact same entry as the vulnerable application.
The alternatives are constrained only by our creativeness. Below are just a few examples:
- Inject code into banking purposes to seize credentials, and at the exact same time have SMS permissions to steal the Two-Variable Authentication (2FA) codes.
- Inject code into Organization apps to achieve access to company means.
- Inject code into social media programs to spy on the target, and use spot accessibility to track the unit.
- Inject code into IM apps to seize all messages, and possibly send messages on the victim’s behalf.
Observing is believing
To exhibit an exploit, Check Point utilized a evidence-of-strategy destructive app to steal an authentication cookie from an outdated model of Chrome. With possession of the cookie, the attacker is then able to obtain unauthorized entry to a victim’s Dropbox account.
https://www.youtube.com/check out?v=Dfa8JEvnteY
Account Takeover exploiting vulnerability in Android’s Play Main Library Code – Demo.
Test Point recognized 14 apps with mixed downloads of pretty much 850 million that remained vulnerable. Inside of a few hours of publishing a report, the protection agency reported that developers of some of the named applications had released updates that fastened the vulnerability.
Apps identified by Examine Place incorporated Edge, XRecorder, and the PowerDirector, which have combined installations of 160 million. Check Stage furnished no sign that any of these apps had been fixed. Ars asked builders of all three applications to remark on the report. This put up will be current if they respond.





More Stories
eSIMs for Tourists of India
(CETX), (CSCW) – 12 Details Technological know-how Shares Relocating In Wednesday’s After-Current market Session
(BRQS), (CLSK) – 12 Information Technologies Shares Moving In Wednesday’s Right after-Market place Session